Flies are not only annoying pests but also carriers of diseases, making fly control an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy and hygienic environment. Understanding the basics of fly control, identifying common fly infestation areas, implementing proactive measures, and adopting integrated pest management techniques are all crucial steps in preventing fly infestations. By following these strategies, you can effectively control flies and create a safer and more comfortable living or working space.
Understanding the Basics: The Importance of Fly Control
Fly control is not just about eliminating a nuisance; it is a matter of public health and safety. Flies are known to transmit various diseases, including salmonella, E. coli, and cholera. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), flies are responsible for spreading over 65 diseases worldwide. These diseases can be transmitted through fly contact with food, surfaces, or even direct contact with humans.
Furthermore, flies reproduce rapidly, with a single female fly capable of laying hundreds of eggs in her short lifespan. This rapid reproduction cycle can quickly lead to a full-blown infestation if not addressed promptly. Therefore, understanding the importance of fly control is crucial in preventing the spread of diseases and maintaining a clean and healthy environment.
Identifying Common Fly Infestation Areas: Where to Focus Your Efforts
Flies are attracted to areas where they can find food, water, and suitable breeding conditions. Identifying these common fly infestation areas is key to effectively targeting your fly control efforts. Kitchens, garbage areas, pet waste, and outdoor dining spaces are some of the most common areas where flies thrive.
In kitchens, flies are attracted to uncovered food, dirty dishes, and spills. Garbage areas provide ample food sources for flies, especially if the trash is not properly sealed or disposed of regularly. Pet waste, such as litter boxes or outdoor areas where pets relieve themselves, can also attract flies. Additionally, outdoor dining spaces, such as patios or picnic areas, can become breeding grounds for flies if food scraps and spills are not promptly cleaned up.
By focusing your fly control efforts on these common infestation areas, you can significantly reduce the fly population and prevent future infestations.
Proactive Measures: Effective Strategies for Preventing Fly Infestations
Prevention is always better than dealing with a full-blown infestation. Implementing proactive measures can help prevent fly infestations before they even begin. Here are some effective strategies:
Maintain cleanliness: Regularly clean and sanitize all areas, paying special attention to kitchens, garbage areas, and pet waste. Clean up spills and food debris promptly to eliminate potential food sources for flies.
Proper waste management: Ensure that all garbage cans have tight-fitting lids and are emptied regularly. Keep outdoor trash bins away from entrances and clean them regularly to prevent fly breeding.
Install screens: Use screens on windows and doors to prevent flies from entering your space. Repair any damaged screens to maintain their effectiveness.
Eliminate standing water: Flies are attracted to standing water, which serves as a breeding ground. Regularly empty and clean bird baths, gutters, and any other areas where water may accumulate.
Integrated Pest Management: A Holistic Approach to Fly Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive and environmentally friendly approach to pest control, including fly control. It focuses on long-term prevention and management rather than relying solely on chemical treatments. IPM combines various strategies to control flies, including:
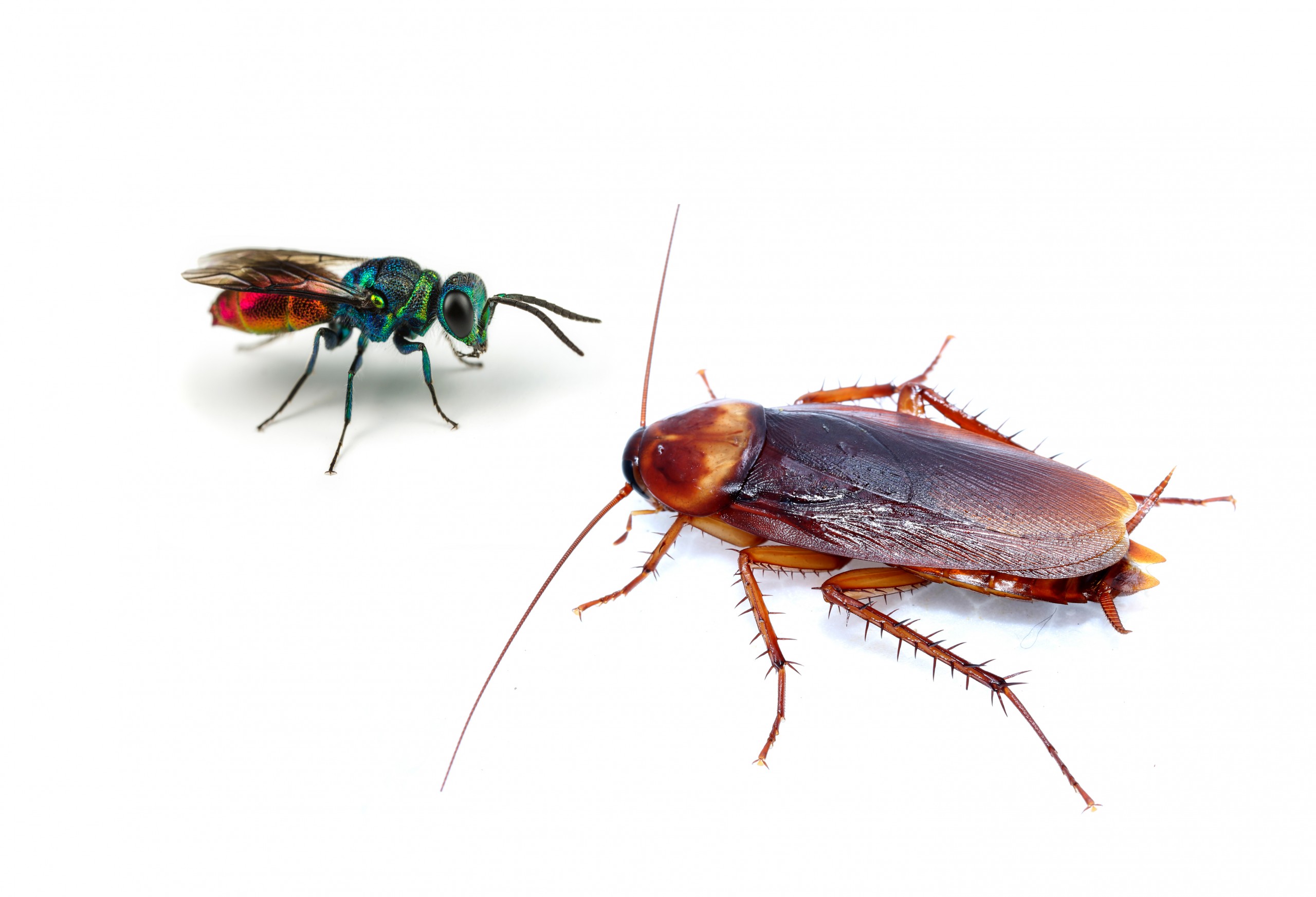
Biological control: Introducing natural predators of flies, such as parasitic wasps or fly predators, can help reduce the fly population without the use of chemicals.
Physical control: Implementing physical barriers, such as fly traps or sticky tapes, can help capture and control flies. These methods are non-toxic and can be used in conjunction with other control measures.
Chemical control: As a last resort, chemical control methods can be used. However, it is important to use these methods judiciously and follow all safety guidelines to minimize environmental impact.
Regular monitoring: Regularly inspecting and monitoring fly activity can help identify infestations early on and allow for prompt action.
By adopting an integrated pest management approach, you can effectively control flies while minimizing the use of harmful chemicals and promoting a healthier environment.
In conclusion, fly control is essential for maintaining a clean and healthy environment. Understanding the basics of fly control, identifying common infestation areas, implementing proactive measures, and adopting integrated pest management techniques are all key strategies in preventing fly infestations. By following these strategies, you can effectively control flies and reduce the risk of disease transmission, creating a safer and more comfortable space for all.