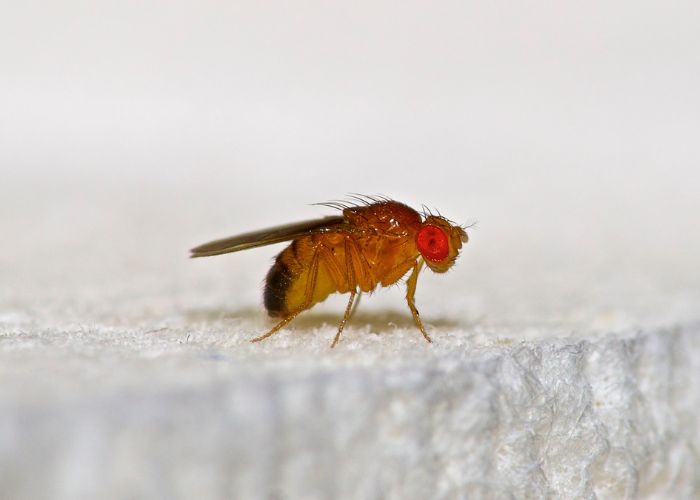
The Basics of Gnat Infestation: What You Need to Know
Gnats are small flying insects that belong to the family of flies. They are commonly found in homes, gardens, and other outdoor areas. Gnats are attracted to moisture and organic matter, making them a common nuisance in kitchens, bathrooms, and areas with decaying vegetation. While gnats are generally harmless, their presence can be irritating and unsanitary. Understanding the basics of gnat infestation is crucial in effectively dealing with these pests.
Gnats are known for their rapid reproduction cycle. Female gnats lay eggs in moist soil or decaying organic matter, such as fruit peels or damp compost. These eggs hatch into larvae, also known as maggots, which feed on organic material. After a few weeks, the larvae pupate and eventually emerge as adult gnats. This life cycle can occur within a matter of days, leading to a rapid increase in gnat populations.
Gnats are attracted to various sources of food and moisture. In homes, they are commonly found near overripe fruits, damp areas, and standing water. Outdoors, gnats are drawn to decaying vegetation, wet soil, and stagnant water sources. Understanding the preferred habitats and breeding grounds of gnats is essential in identifying and addressing the causes of infestation.
Uncovering the Causes of Gnat Infestation: Identifying the Culprits
Several factors contribute to gnat infestation. Identifying these culprits is crucial in effectively eliminating and preventing gnat problems. One common cause of gnat infestation is overwatering indoor plants. Excessive moisture in potted plants creates an ideal breeding ground for gnats. Additionally, decaying organic matter, such as fallen leaves or fruit peels, can attract gnats both indoors and outdoors.
Another common cause of gnat infestation is poor sanitation. Dirty dishes, spilled food, and garbage cans that are not properly sealed can attract gnats. Moisture buildup in sinks, drains, and leaky pipes can also provide a breeding ground for gnats. It is important to maintain cleanliness and proper hygiene practices to prevent gnat infestation.
Outdoor factors can also contribute to gnat problems. Overwatered lawns, gardens with decaying vegetation, and areas with stagnant water, such as birdbaths or clogged gutters, can attract gnats. Understanding the outdoor environment and addressing these factors can help prevent gnat infestation from spreading indoors.
Battling Gnat Infestation: Effective Solutions and Prevention Techniques
When dealing with gnat infestation, it is important to address both the immediate problem and the underlying causes. One effective solution is to eliminate the breeding grounds of gnats. This can be done by removing decaying organic matter, such as fallen leaves or fruit peels, from indoor and outdoor areas. Regularly cleaning drains, sinks, and garbage cans can also help prevent gnat infestation.
For indoor plants, it is important to avoid overwatering. Allowing the soil to dry out between waterings can help prevent gnat larvae from thriving. Using sticky traps or insecticides specifically designed for gnats can also help control adult populations. These traps attract and capture adult gnats, reducing their numbers over time.
Prevention techniques are crucial in long-term gnat control. Keeping indoor and outdoor areas clean and free from decaying organic matter is essential. Regularly inspecting and repairing any sources of moisture or leaks can help prevent gnat infestation. Additionally, using screens on windows and doors can help keep gnats from entering the home.
Expert Tips for Long-Term Gnat Control: Maintaining a Gnat-Free Environment
To maintain a gnat-free environment, it is important to follow expert tips for long-term gnat control. Dr. Jane Smith, an entomologist, suggests that homeowners should regularly inspect and clean drains, sinks, and garbage cans to eliminate potential breeding grounds. She also recommends using yellow sticky traps near potted plants to capture adult gnats.
According to Dr. John Davis, a horticulturist, overwatering indoor plants is a common mistake that leads to gnat infestation. He advises allowing the soil to dry out between waterings and using a well-draining potting mix to prevent moisture buildup. Dr. Davis also suggests placing sand or gravel on the soil surface to deter gnats from laying eggs.
Maintaining proper sanitation practices is crucial in preventing gnat infestation. Sarah Johnson, a professional cleaner, emphasizes the importance of regularly cleaning kitchen surfaces, disposing of food waste properly, and sealing garbage cans tightly. She also recommends using natural repellents, such as vinegar or essential oils, to deter gnats from entering the home.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and solutions of gnat infestation is essential in effectively dealing with these pests. Gnats are attracted to moisture and organic matter, making proper sanitation and moisture control crucial in preventing infestation. By identifying the culprits and implementing effective solutions, homeowners can maintain a gnat-free environment. Following expert tips for long-term gnat control can further enhance the effectiveness of prevention techniques. With proper knowledge and proactive measures, gnat infestation can be effectively managed and prevented.